WHY US

Multiple Locations
Monarch Dentistry has 13 locations across Southern Ontario. For your convenience, we'll transfer files from office to office to visit any location!

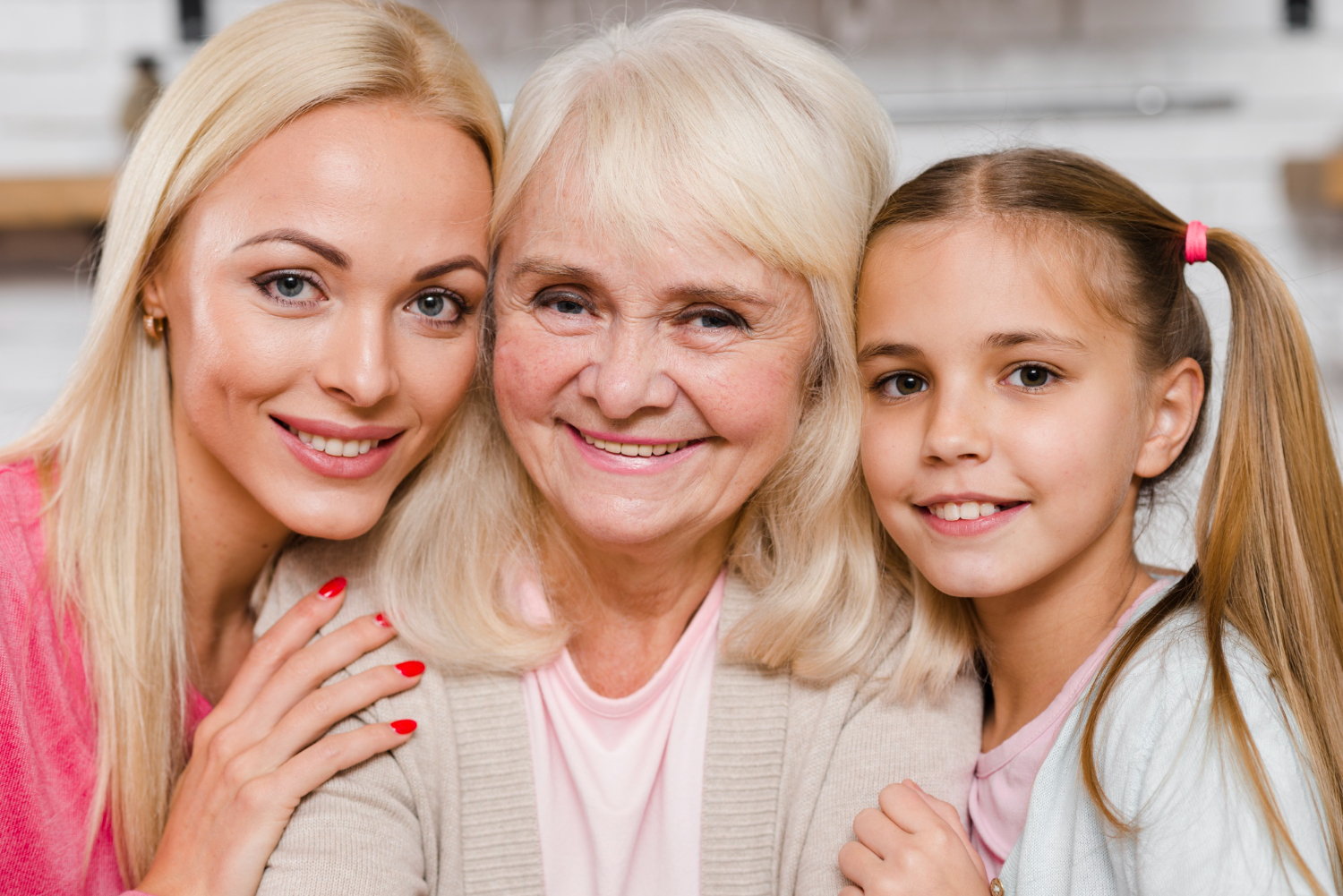
Family Friendly
Our highly-trained staff can provide quality dental care for your entire family! Drop by the Monarch Dentistry nearest you to receive the treatment.


Advanced Technology
We utilize state-of-the-art technology in order to provide all of our patients with the best dental experience possible.


Friendly Staff
Our dental team is made up of experienced professional dentists and hygienists who understand your smile.